Explain Different Types of Photochemical Reactions
Thermal and photochemical reactions Thermal reactions. The energy that these molecules carry is stored in a bond that holds a single atom to the molecule.
Those reactions in which two compounds by the exchange of ions to form two new compound are called double displacement reactions.

. In fireflies an enzyme in the abdomen catalyzes a reaction that produced light. Photosynthesis Bioluminescence Photo-degradation Vision Photo-alkylation. Types of photochemical reactions.
Since it is the electrons that provide the bonding forces that hold atoms together into molecules if the distribution of electrons within a molecule changes drastically the. When a larger molecule is formed from simple ones c Photosensitized reactions when an excited molecule supplies activation energy for the reactants. Sources of primary radicals include the photolysis of ozone aldehydes RCHO and nitrous acid HONO while the decomposition of VOCs due to reactions with OH provides a source of secondary radicals RO x which then lengthen the radical and NO x.
Thus for example water can be added to a carboncarbon double bond as a step in the breakdown of many different compounds including sugars lipids and amino acids. Types of Photochemical Reactions 1. Plants use solar energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
CuSO 4 aqZnsZnSO 4 aqCus In this reaction zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate solution. The 5 primary types of chemical reactions are. The photoreaction starts from the ground state of the reactant s necessarily proceeds via electronically excited state s and ends with the product s in the ground state.
The consequence of molecules absorbing light is the creation of transient excited states whose chemical and physical properties differ greatly from the original molecules. The black circles and arrows indicate the different steps of the photochemical experiment. Presence of light is the primary requirement.
In terms of oxygen transfer oxidation is a gain of oxygen. Some examples of this form of reactions are as follows. The most important use of oxidation is described in terms of electron transfer.
Oxidation can also be defined as a loss of hydrogen. Photochemical smog is also referred to as oxidizing smog. Therefore photochemical reactions inevitably include diabatic processes ie a transition from one potential surface to another.
Norrish type i the norrish type ii the racemization of optically active biphenyls the type a cyclohexadienone rearrangement the type b cyclohexenone rearrangement the di-pi-methane rearrangement the type b bicyclo 310hexanone rearrangement to phenols photochemical electrocyclic processes. If a reaction releases energy and heat it is. 7 rows Different Types of Chemical Reactions.
Such processes can be characterized by the type of chemistry induced by light absorption. The immediate consequence of light absorption is a primary photochemical reaction. Photochemical reaction a chemical reaction initiated by the absorption of energy in the form of light.
The yield is quantitative. College Jogeshwari E Maharashtra 400060. 1 initial state of the system in the FranckCondon region 2 photoexcitation from S 0 to S 1 triggered by a laser pulse 3 relaxation through a conical intersection and 4 formation of.
One type of photochemical reaction is the dissociation of a molecule into two fragments. These reactions can take place in light as well as in dark. The complexity of life results not from many different types of reactions but rather from these simple reactions occurring in many different situations.
Oxetene Formation Paterno-Buchi Reaction O O O O O O H Ar H Ar H H O H H H Ar O hv hv Photochemical Reactions of Alkene and Dienes Isomerization 1. A double displacement reaction usually occurs in solution and one of the products being. Trans compound has longer absorption wavelength 2.
Indeed one of the classic photochemical reactions of organic chemistry is the formation of 1122-tetraphenyl-12-ethanediol 3 benzopinacol by the action of light on a solution of diphenylmethanone 2 benzophenone in isopropyl alcohol. Human formation of vitamin D by exposure to sunlight. These new chemical species can fall apart change to new structures combine with each other or other.
Both cis and trans give the same excited state species twisted geometry with 90o rotation of p-orbital relative to each other CC CC λmax 200nm hv πÆπ. This is a model for the photochemical crosslinking of DNA and proteins by UV radiation see the Module on DNA-Protein Crosslinks. 16 rows Photochemical Reactions Alkene Isomerization A photochemical reaction occurs when internal conversion and relaxation of an excited state leads to a ground state isomer of the initial substrate molecule or when an excited state undergoes an intermolecular addition to another reactant molecule in the ground state.
These reactions involve absorption or evolution of heat energy. Common organic photochemical reactions include. For ATP it is a phosphate atom and for NADPH it is a hydrogen atom.
A Photodissociation b Photosynthesis. Of these photodissociation is by far the most pervasive and important in atmospheric chemistry. In the light-dependent reactions energy absorbed by sunlight is stored by two types of energy-carrier molecules.
Difference between Photochemical and thermal Reaction- Photochemical Reaction Thermal Reaction These reactions involve absorption of light radiations. 080418 1 Shri Bapu R. Oxidation reactions have been defined several ways.
Thermochemistry is the study of the energy and heat associated with chemical reactions. Linear addition to an unsaturated molecule eg the pyrimidine base thymne in DNA can combine with the amino acid residue cysteine in proteins. Photolysis is the process by which a photochemical reaction is performed.
Photodissociation intramolecular rearrangements photoisomerization photodimerization hydrogen atom abstraction and photosensitized reactions. Professor of Chemistry Govt. Secondary reactions are termed subsequent chemical shifts.

Photochemical Reaction Definition Examples Applications

Photochemical Reaction Definition Examples Applications

Photochemical Reaction Definition Examples Applications
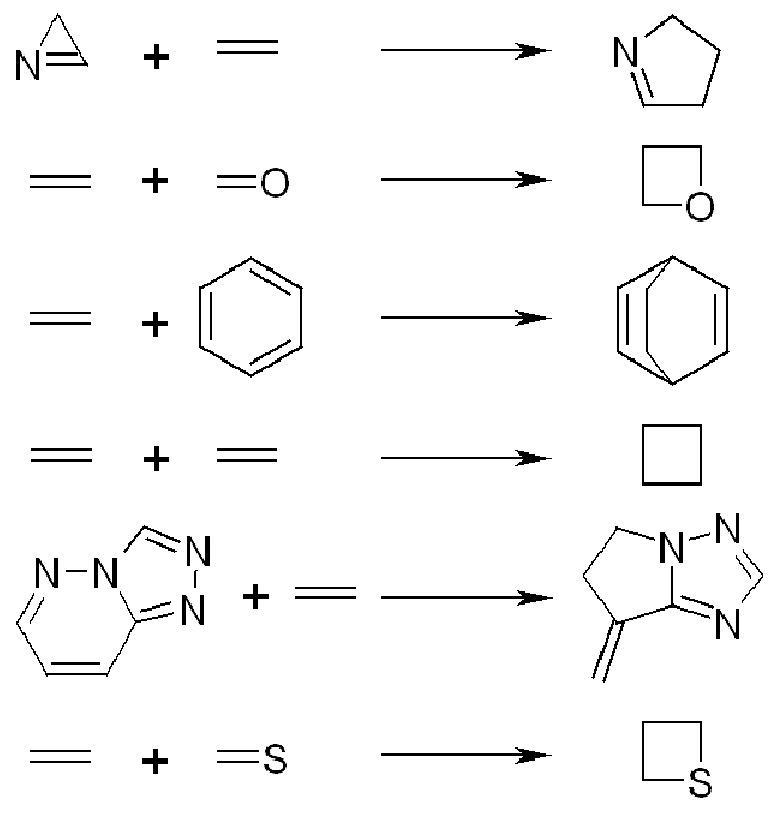
Types Of Photochemical Reactions From Top 3 2 Photocycloaddition Of Azirines To C C 2 2 Photocycloaddition Of C C To C O 4 2 And 4 4 Photocycloaddition Of Olefins To Carbon Only
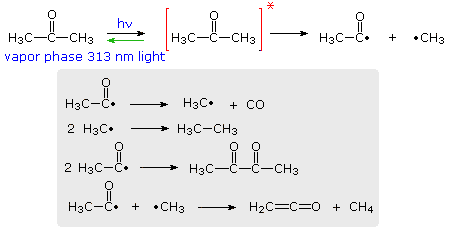
Comments
Post a Comment